Biochemistry Pathophysiology and Regulation Biology Diagrams Ubiquitin is an ubiquitously expressed small regulatory protein in living cells [].The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination, which is catalyzed by three types of
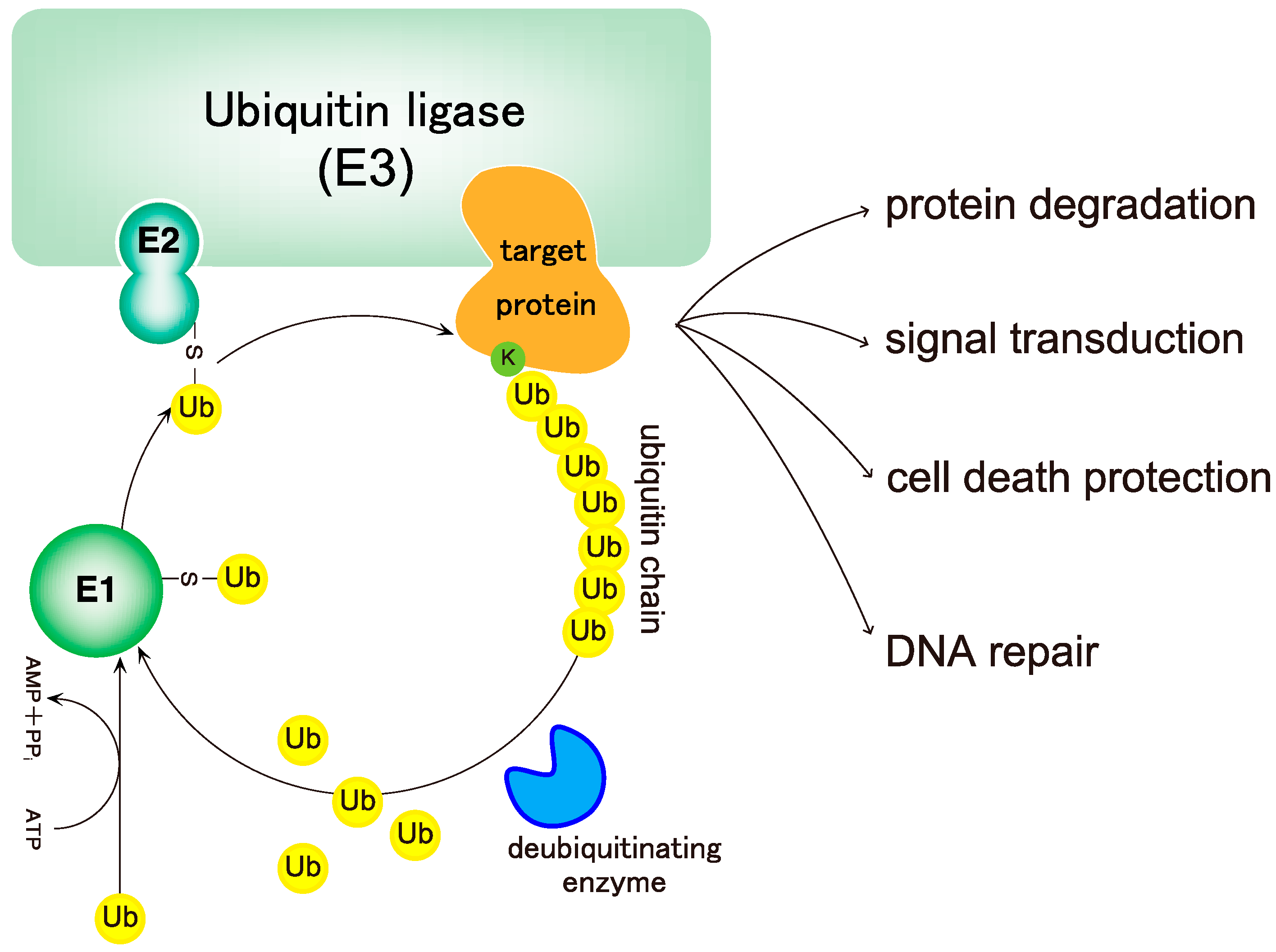
Besides tagging proteins for degradation, ubiquitin is now recognized as a signaling module for diverse cellular processes, including progression through the cell cycle, DNA repair, gene transcription, receptor trafficking and endocytosis. Recent advances have indicated the existence of a wide varie …

The role of ubiquitination in health and disease Biology Diagrams
The small protein ubiquitin plays a vital role in virtually all aspects of cellular life. Among the diverse signaling outcomes associated with ubiquitination, the most well-established is the targeted degradation of substrates via the proteasome. During cell growth and proliferation, ubiquitin plays an outsized role in promoting progression through the cell cycle.

The ubiquitin-proteasome system plays a pivotal role in the sequence of events leading to cell division known as the cell cycle. Not only does ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis constitute a critical component of the core oscillator that drives the cell cycle in all eukaryotes, it is also central to the mechanisms that ensure that the integrity of the genome is maintained. Several ubiquitin ligases are altered in cancer. These proteins are crucial for the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cell-cycle proteins, ensuring regulated progression through the cycle.
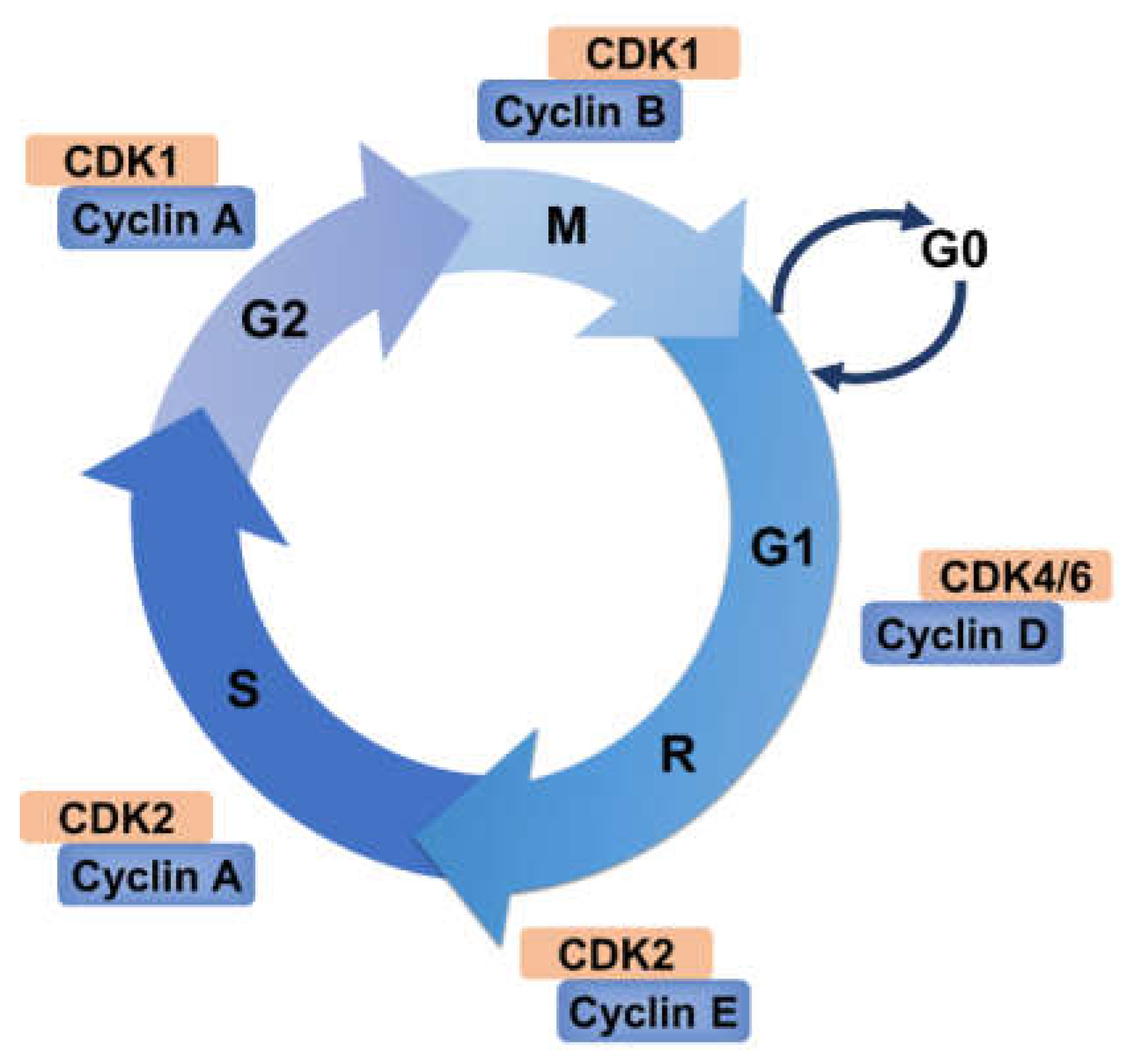
Ubiquitin signaling in cell cycle control and tumorigenesis Biology Diagrams
The SAC generates a diffusible "wait anaphase" signal through unattached kinetochores. 162 In securin‐deficient cells, researchers have identified human shugoshin 2 (Sgo2), which forms a complex with mitotic‐arrest deficient‐1 (Mad2), substituting the role of securin in these cells. 163 The interplay between APC/C, the SAC, and early
